The desire to preserve youthful skin has long shaped the skincare industry, and among the myriad of ingredients promoted as solutions for aging, few have undergone the level of scientific scrutiny and clinical validation that tretinoin has. Often known under the brand name Retin-A, this prescription-strength retinoid has earned a formidable reputation for its powerful effects on wrinkles and other visible signs of skin aging. As our understanding of dermatological science deepens, so too does our insight into how tretinoin works at a cellular level to rejuvenate skin. This article explores the proven anti-aging mechanisms of tretinoin, examining both the biological processes it targets and the real-world results that support its efficacy.
You may also like: How to Choose Skin Care for Fine Lines: Evidence-Based Tips for Healthier, Younger-Looking Skin
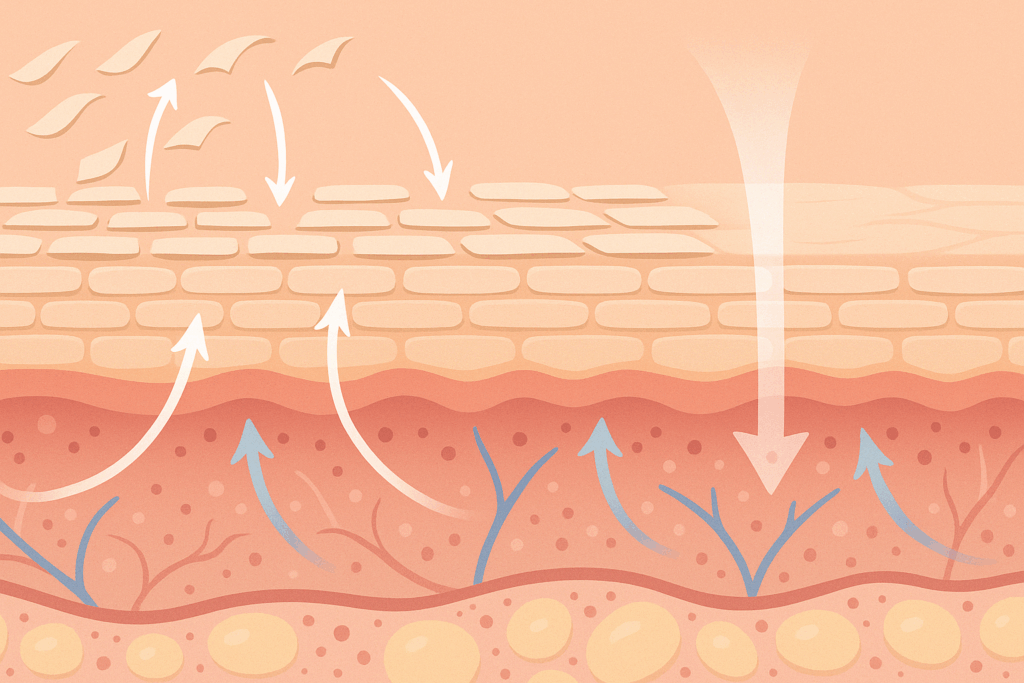
Understanding What Retin-A Is and What It Does
To understand how tretinoin works for wrinkles, it’s essential to first answer the common question: what is Retin-A? Retin-A is a topical formulation of tretinoin, a derivative of vitamin A that is categorized under retinoids. It was initially developed for the treatment of acne but soon gained attention for its remarkable ability to improve skin texture, reduce fine lines, and promote a more even tone. Scientifically speaking, what Retin-A does is stimulate rapid cell turnover, which encourages the shedding of old, damaged skin cells while promoting the development of new, healthy ones. This dual action forms the basis of its wrinkle-reducing properties.
Beyond exfoliation, tretinoin penetrates deep into the dermis, where it enhances collagen synthesis. Collagen is the protein scaffold that gives skin its firmness and elasticity, but its production declines with age. By activating collagen production and reducing its breakdown, tretinoin strengthens the skin’s structural integrity. Moreover, tretinoin helps prevent the degradation of existing collagen by inhibiting enzymes like matrix metalloproteinases, which are often upregulated in sun-damaged skin. As a result, users often observe noticeable improvements in skin firmness, tone, and texture.
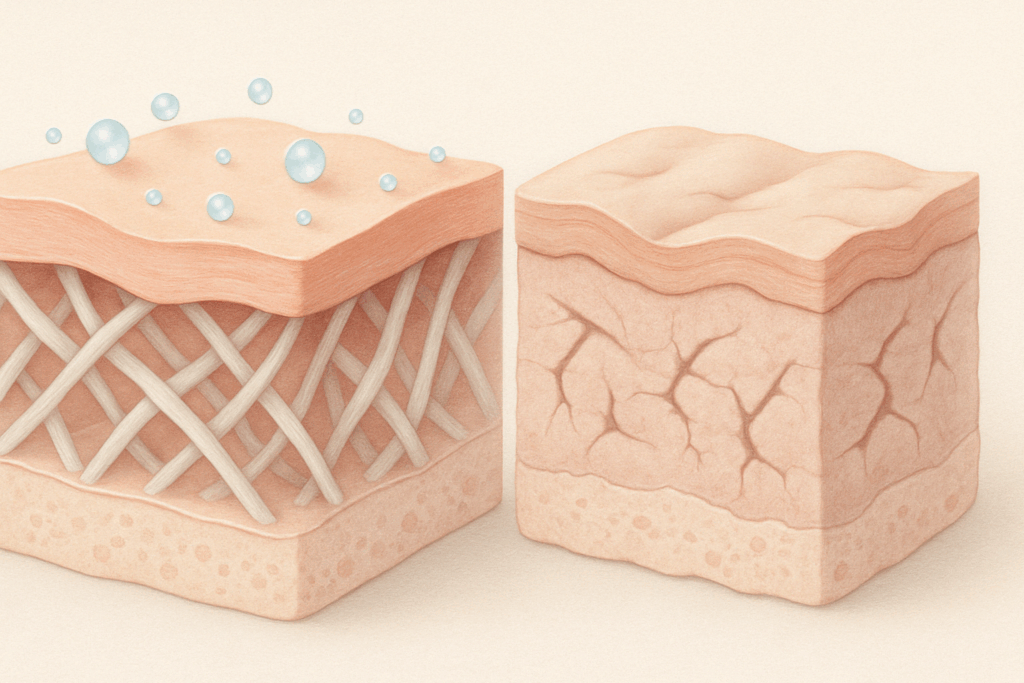
The Science Behind Tretinoin and Its Anti-Aging Power
Numerous peer-reviewed studies have validated the anti-aging properties of tretinoin, establishing it as the gold standard among topical treatments for photoaging. Tretinoin anti-aging effects are mediated through its interaction with nuclear receptors in skin cells, particularly the retinoic acid receptors (RARs). When tretinoin binds to these receptors, it activates gene expression pathways that regulate cell differentiation and proliferation. These changes, in turn, enhance epidermal thickness and stimulate fibroblasts to produce new collagen fibers.
One of the most critical aspects of how tretinoin works is its impact on dermal remodeling. With consistent use, tretinoin promotes the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, such as hyaluronic acid, which help the skin retain moisture and maintain a plump appearance. This rehydration effect complements the firming benefits conferred by increased collagen, offering a multifaceted improvement in skin texture and elasticity. Importantly, tretinoin also helps to normalize melanocyte activity, thereby reducing hyperpigmentation and improving overall skin tone—a valuable bonus in anti-aging skincare.
Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated the efficacy of tretinoin cream for wrinkles. One landmark study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology reported that daily use of tretinoin resulted in significant improvements in fine and coarse wrinkles, skin roughness, and mottled hyperpigmentation over a six-month period. These tretinoin results for wrinkles were not only statistically significant but also clinically meaningful, reinforcing its role as a cornerstone in dermatologic anti-aging protocols.
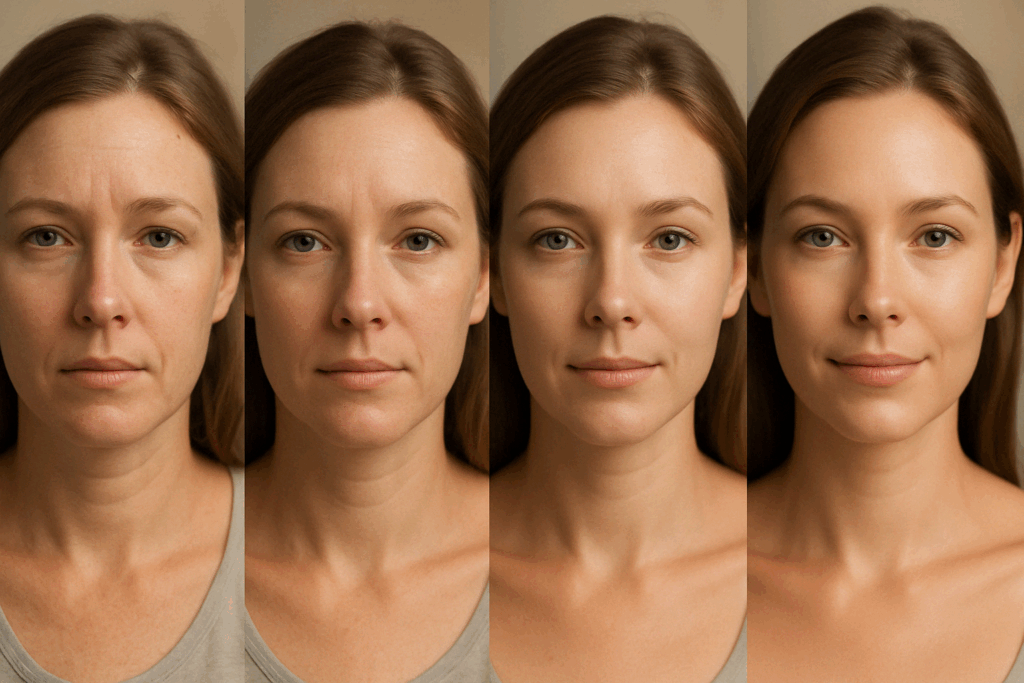

Retin-A Results: What to Expect with Continued Use
For individuals curious about what Retin-A results they can expect, the journey requires both consistency and patience. Initial changes typically begin with increased skin exfoliation, which may be accompanied by mild irritation or dryness. These early effects are common as the skin adjusts to the increased cell turnover promoted by tretinoin. Over time, however, most users begin to notice a reduction in fine lines, improved skin texture, and a more radiant complexion.
In studies evaluating long-term use, the benefits of tretinoin aging interventions appear to compound. Over a 12-month span, skin biopsies reveal measurable increases in collagen content and reductions in atypical keratinocyte patterns associated with sun damage. These cellular changes translate into visibly smoother, firmer, and more youthful skin. Importantly, when used under the guidance of a qualified dermatologist, Retin-A can deliver sustained anti-aging benefits without the need for invasive procedures.
It’s worth noting that tretinoin is available in various strengths, including the commonly prescribed Retin-A 0.05%. Dermatologists often recommend starting with a lower concentration to minimize irritation, gradually increasing as the skin builds tolerance. Whether used on the face or the neck—areas particularly prone to visible aging—tretinoin has proven efficacy. The use of Retin-A for neck rejuvenation is gaining popularity, as the neck’s thinner skin often exhibits wrinkles and laxity sooner than the face. Applying tretinoin to this area can promote smoother, firmer skin when used with appropriate moisturizers and sun protection.

How to Use Retin-A for Wrinkles Safely and Effectively
Proper application is essential to achieving optimal results while minimizing side effects. For those wondering how to use Retin-A for wrinkles, dermatologists typically advise beginning with a pea-sized amount applied to clean, dry skin once every other night. This approach allows the skin to acclimate to the medication gradually. Moisturizers can be applied afterward to buffer potential dryness or flaking, which are common in the early stages of treatment.
Because tretinoin increases skin sensitivity, especially to ultraviolet radiation, it is vital to apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily and limit sun exposure. Failing to do so not only undermines the anti-aging benefits but can also exacerbate irritation and lead to further pigmentation issues. Patients should also be cautious when combining tretinoin with other active ingredients such as alpha hydroxy acids or benzoyl peroxide, as these combinations can amplify irritation unless carefully managed.
Understanding how often to use tretinoin for anti-aging is another key to success. While some patients tolerate daily application, others benefit from alternate-night dosing. Ultimately, the goal is to find a sustainable routine that delivers consistent improvements without causing undue discomfort. Most users begin to see improvements in skin smoothness and tone within eight to twelve weeks, with more dramatic reductions in wrinkles emerging over several months.
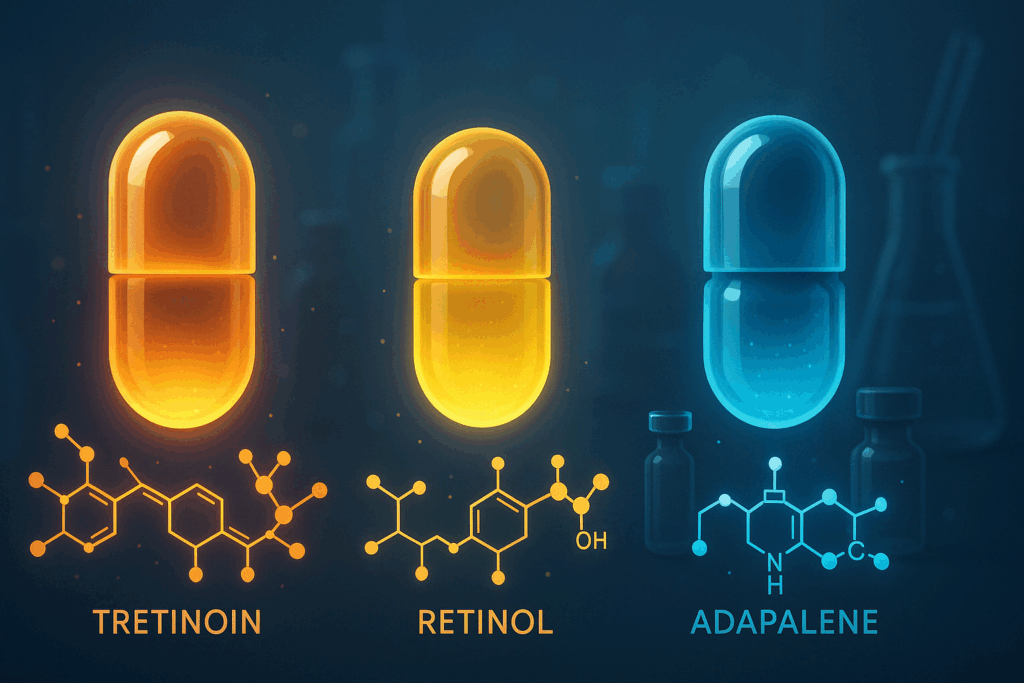
Comparing Tretinoin to Other Retinoids: Is It the Best Choice?
The skincare market is saturated with over-the-counter retinoids, but not all are created equal. While retinol—available in many non-prescription formulations—can offer mild anti-aging benefits, it is significantly less potent than tretinoin. This distinction is important when answering questions like: does retinol help with wrinkles, or is tretinoin good for wrinkles? Retinol must undergo enzymatic conversion within the skin to become active, while tretinoin is already in its active form, allowing it to work more efficiently and effectively.
Differin (adapalene) is another retinoid often discussed in the context of anti-aging. Originally developed for acne, Differin has demonstrated some wrinkle-reducing capabilities in clinical studies. However, the question remains: does Differin help with wrinkles as effectively as tretinoin? Most dermatologists agree that while Differin may offer some benefits, tretinoin remains the superior option for addressing advanced signs of aging. That said, for those with highly sensitive skin, Differin can be a useful starting point, especially when the goal is to introduce retinoids gently.
The category of retinoids for wrinkles encompasses a wide range of formulations, but tretinoin remains the benchmark for efficacy. This is due in large part to its extensive history of clinical use, robust safety profile, and ability to deliver long-term structural changes in the skin. Whether choosing tretinoin cream for wrinkles or a milder alternative, the key is to ensure that the product is formulated for optimal skin penetration and used consistently over time.
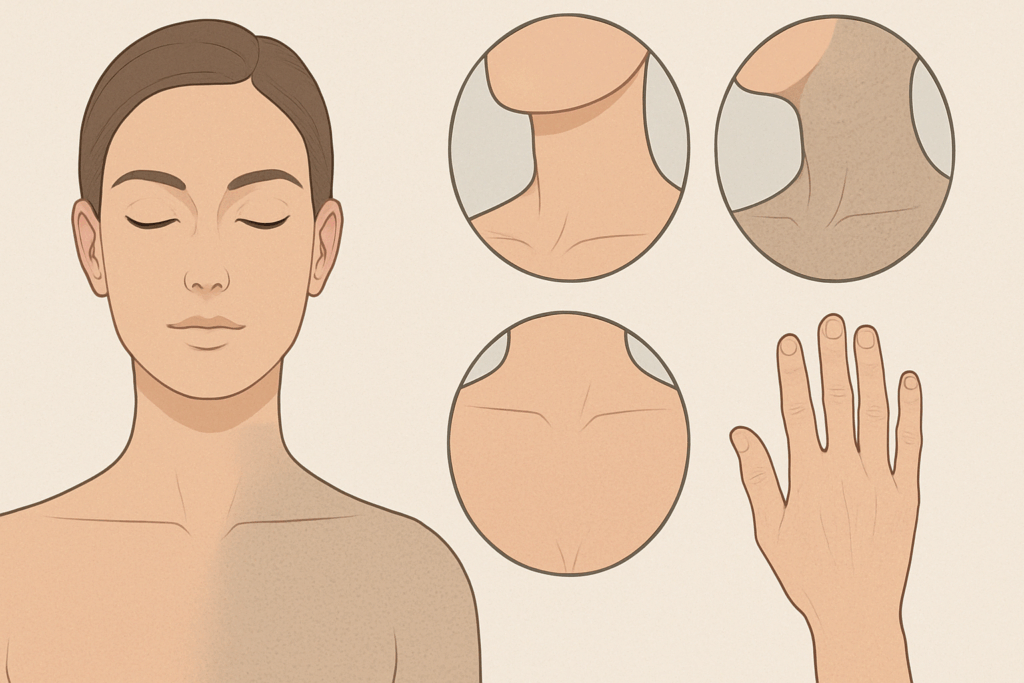
Exploring the Role of Tretinoin in Specific Conditions
While often discussed in the context of facial aging, tretinoin is also employed to treat conditions such as actinic keratosis and keratosis pilaris, particularly when used as Retin-A for face keratosis. These precancerous lesions are typically caused by long-term sun exposure and are a known risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma. Tretinoin can help reduce the appearance of these lesions by encouraging rapid cell turnover and exfoliation, thereby minimizing the accumulation of abnormal cells.
Similarly, the use of Retin-A for neck rejuvenation has grown as consumers seek comprehensive anti-aging regimens that address more than just the face. The skin on the neck is especially susceptible to fine lines and crepey texture, making it an ideal candidate for tretinoin-based interventions. With careful application and sun protection, users can achieve meaningful improvements in skin tone and firmness.
Another emerging use involves retinal skin care routines that incorporate tretinoin or related derivatives to target signs of photoaging across multiple areas. From the chest to the hands, tretinoin aging protocols can be adapted to suit individual needs, provided users apply the product correctly and monitor for signs of irritation. Whether addressing sun spots, fine lines, or textural irregularities, tretinoin offers a flexible, science-backed approach.
Balancing Expectations with Evidence: What Can Tretinoin Realistically Do?
A crucial component of any discussion about tretinoin is setting realistic expectations. While it is true that tretinoin cream anti-aging effects can be profound, they are rarely instantaneous. Instead, the process unfolds gradually, often requiring weeks or even months to manifest fully. This slow, cumulative improvement is a hallmark of how tretinoin works—it doesn’t offer a quick fix but rather a sustainable transformation over time.
For those asking questions such as “will Retin-A help wrinkles?” or “can Retin-A tighten skin?” the answer lies in understanding its mechanism of action. Tretinoin does not physically pull or tighten the skin like a surgical lift, but it does thicken the epidermis and rebuild collagen within the dermis, leading to visibly firmer, more youthful skin. In clinical evaluations, patients using tretinoin reported improvements in skin elasticity and tone, often noting a more lifted appearance, particularly when used consistently alongside complementary skincare strategies.
There is also compelling evidence that tretinoin helps delay the development of new wrinkles, not just minimize existing ones. By protecting and restoring collagen and supporting healthy cell function, it serves as both a corrective and preventive treatment. This dual function is especially valuable for individuals seeking a long-term anti-aging solution grounded in robust scientific evidence.
Frequently Asked Questions: Tretinoin, Retin-A, and Anti-Aging Skin Care
1. How does using Retin-A for face keratosis differ from using it for wrinkles?
While Retin-A is frequently prescribed for both wrinkles and keratosis, its action varies subtly depending on the target condition. In the case of face keratosis—particularly actinic keratosis—Retin-A works to normalize atypical skin cell growth, which helps reduce precancerous lesions. When used for wrinkles, its main benefit lies in stimulating collagen and promoting skin turnover for cosmetic rejuvenation. Unlike cosmetic applications, treating face keratosis with Retin-A may require longer treatment cycles and closer dermatologic supervision. Still, the ability of Retin-A to enhance skin clarity and reduce scaly patches shows just how versatile it is for addressing both medical and aesthetic skin concerns.
2. Can tretinoin for wrinkles be safely combined with other anti-aging products?
Yes, but thoughtful integration is essential. When using tretinoin for wrinkles, combining it with peptides, niacinamide, or hyaluronic acid can enhance skin hydration and support barrier repair without diminishing efficacy. However, using tretinoin cream for wrinkles alongside other potent actives like AHAs, BHAs, or benzoyl peroxide requires caution, as these can increase irritation. If you’re layering products, apply tretinoin after your moisturizer at night to buffer potential dryness. Dermatologists often recommend alternating nights between tretinoin and exfoliants to preserve skin health while maximizing anti-aging benefits.
3. What does Retin-A do for skin in your 60s or 70s compared to earlier decades?
Retin-A continues to be effective into older adulthood, although the visible response may differ from younger users. In your 60s or 70s, what Retin-A does is maintain dermal thickness, improve age spots, and reduce the depth of entrenched wrinkles. Collagen production slows significantly with age, so tretinoin aging protocols may work more gradually, but studies still confirm benefits even in septuagenarians. Patients at this stage often benefit from lower concentrations like Retin-A 0.05% to reduce irritation. Importantly, the long-term use of tretinoin cream for wrinkles in mature skin helps maintain skin integrity and may delay the need for more invasive cosmetic interventions.
4. Does Differin help with wrinkles as effectively as prescription tretinoin?
Differin (adapalene) is a synthetic retinoid that is FDA-approved for acne but has shown mild anti-aging effects in some studies. That said, the answer to whether Differin helps with wrinkles depends on individual skin sensitivity and the severity of photoaging. Differin is generally gentler than tretinoin and may be better tolerated for beginners or those with rosacea-prone skin. However, for advanced aging concerns, tretinoin cream for wrinkles tends to offer more dramatic results, particularly when it comes to dermal remodeling. While Differin can be part of a long-term regimen, tretinoin anti-aging benefits are typically superior in terms of collagen regeneration and wrinkle depth reduction.
5. Is tretinoin good for wrinkles in individuals with darker skin tones?
Yes, but it should be introduced thoughtfully. Tretinoin is good for wrinkles across all skin tones, but individuals with higher Fitzpatrick types may be more prone to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation during the initial adjustment phase. To mitigate this, dermatologists often recommend starting with a lower concentration of tretinoin cream anti-aging products and pairing it with non-comedogenic moisturizers and sunscreen. Over time, tretinoin not only softens wrinkles but also improves melanin distribution, reducing dark spots and enhancing radiance. The key is to build tolerance slowly and avoid over-exfoliation.
6. What are the psychological benefits of seeing Retin-A results over time?
Beyond the physical improvements in skin, Retin-A results can significantly impact psychological well-being. For many individuals, reducing wrinkles with tretinoin enhances self-confidence, which positively influences social interactions and self-image. There’s also a cognitive shift when people feel proactive about aging—they often adopt healthier habits overall. Moreover, achieving visible changes through consistent use reinforces patience and discipline, which can translate into other wellness behaviors. The process of engaging in a structured skin routine, such as learning how to use Retin-A for wrinkles correctly, creates a sense of agency and control over the aging process.
7. Can Retin-A tighten skin, or is that a misconception?
The belief that Retin-A can tighten skin is partially accurate but often misunderstood. Retin-A doesn’t physically pull the skin tighter; rather, it stimulates dermal collagen production, which gradually restores firmness and elasticity. So while Retin-A does help with wrinkles and sagging, it won’t replicate the lifting effects of surgery or devices like radiofrequency. However, in long-term users, skin often appears tighter due to improved texture, increased thickness, and hydration retention. Patients seeking to enhance results often combine Retin-A for neck treatment with other firming modalities like microneedling or ultrasound-based therapies.
8. What are some emerging research directions in tretinoin aging applications?
Exciting developments are underway regarding how tretinoin works synergistically with novel delivery systems like nanocarriers and liposomes. These innovations aim to reduce irritation and improve penetration, particularly for areas like the delicate under-eye or neck. There’s also growing interest in microdosing protocols—applying tretinoin in smaller amounts more frequently—which may preserve skin integrity while delivering long-term anti-aging outcomes. Researchers are also exploring combination regimens that pair tretinoin cream anti-aging strategies with growth factors or topical antioxidants. These emerging techniques could refine how often to use tretinoin for anti-aging without compromising skin health.
9. Is there an optimal time to begin tretinoin for wrinkles to maximize long-term benefits?
Starting tretinoin for wrinkles earlier—often in the late 20s or early 30s—can help delay the onset of visible aging, especially when used preventively. Collagen degradation begins in the mid-20s, so introducing tretinoin anti-aging routines before deep wrinkles form provides a proactive advantage. However, there is no upper age limit to benefit; even those starting in their 50s or later can still experience significant improvements. Consistency, sun protection, and realistic expectations are more important than age alone. Establishing when and how often to use tretinoin for anti-aging should be a collaborative decision between patient and dermatologist, tailored to skin type and lifestyle.
10. How does retina skin care differ from general retinoid use in clinical dermatology?
The term “retina skin care” often refers to cosmetic-grade products marketed for general rejuvenation, while dermatologic use of tretinoin, or Retin-A, involves prescription-strength formulations grounded in clinical research. Retina skin care may include over-the-counter retinol or weaker derivatives that require conversion in the skin, whereas tretinoin cream for wrinkles is biologically active upon application. This difference impacts both potency and expected outcomes. For users seeking significant wrinkle reduction, especially in stubborn areas like the neck, using Retin-A for neck treatment under supervision is far more effective than OTC alternatives. The clinical rigor behind prescription retinoids also means they are subject to more stringent safety and efficacy testing, supporting their trusted role in evidence-based dermatologic care.
Final Reflections: Does Tretinoin Help with Wrinkles, and Is It Worth It?
The cumulative body of evidence makes a compelling case: tretinoin is indeed good for wrinkles, and its benefits extend well beyond surface-level improvements. With a consistent routine, scientifically validated results, and a wide range of applications—from facial fine lines to neck sagging and even face keratosis—tretinoin remains a cornerstone of modern anti-aging dermatology. Whether you’re exploring tretinoin for wrinkles for the first time or revisiting its benefits as part of a more advanced regimen, the scientific consensus remains firm: this vitamin A derivative delivers.
Patients interested in exploring tretinoin as a long-term skincare investment should consult with a dermatologist to determine the best concentration and formulation for their skin type. From Retin-A 0.05% to milder or stronger alternatives, tailored guidance ensures both efficacy and comfort. Equally important is adherence to sun protection and the use of supportive skincare, as tretinoin-treated skin is more sensitive to environmental stressors.
Ultimately, the question is not merely whether tretinoin can reduce wrinkles, but how this proven compound can be integrated into a comprehensive strategy for healthy, resilient skin. For those seeking a solution grounded in both science and clinical experience, tretinoin offers a powerful, evidence-based answer. Its ability to stimulate collagen, enhance skin turnover, and improve tone positions it as one of the most trusted tools in the fight against visible aging—delivering not just smoother skin, but renewed confidence in the reflection you see each day.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out
Further Reading:
Topical tretinoin for treating photoaging: A systematic review
How to use tretinoin cream for wrinkles according to a derm
Skin ageing and topical rejuvenation strategies
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While Health11News strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. Health11News, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of Health11News.